
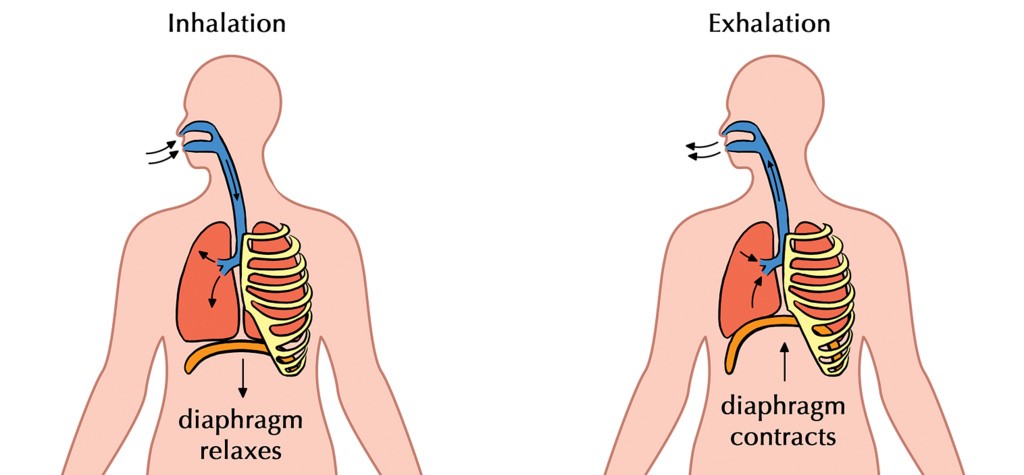

Just as the plueral cavity’s increased negative pressure leads to air uptake during inhalation, the pleural cavity will contract during the exhalation (due to relaxation of the diaphragm),which exerts pressure on the lungs and causes the pressure inside the cavity to be less negative. Because the lung is elastic, it will automatically return to its smaller size as air leaves the lung.Įxhalation begins when inhalation ends. Without surfactant the lungs would collapse at the end of expiration, making it much more difficult to inhale again. The elasticity of the lungs is due to molecules called elastins in the extracellular matrix of lung tissues and is maintained by surfactant, a chemical that prevents the elasticity of the lungs from becoming too great by reducing surface tension from water. The primary reason that expiration is passive is due to the elastic recoil of the lungs. \)Įxhalation (or expiration) is the flow of the respiratory current out of the organism.Įxpiration is typically a passive process that happens from the relaxation of the diaphragm muscle (that contracted during inspiration).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
